January 24, 2026
Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) are reshaping online privacy by shifting data routing from centralized servers to independent, volunteer-operated nodes. Unlike conventional VPNs, dVPNs use blockchain for transparency and end-to-end encryption (E2E) to secure your data. This approach eliminates single points of failure and distributes trust across multiple nodes, enhancing privacy and resistance to censorship. Key features include multi-hop routing, which splits your traffic across several encrypted relays, and the ability to earn cryptocurrency by sharing bandwidth. Solutions like MASQ integrate advanced tools like TLS handshakes, ad blocking, and Web3 compatibility to ensure secure, private, and decentralized internet access.
Key Highlights:
Privacy: Data is encrypted end-to-end and routed through multiple nodes, ensuring no single entity can track your activity.
Censorship Resistance: Thousands of independent nodes eliminate centralized vulnerabilities, making it harder to block the network.
Earn Rewards: Share bandwidth to earn tokens, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem.
Advanced Technology: Features like post-quantum cryptography, TLS encryption, and blockchain-based payment systems ensure security and transparency.
While dVPNs offer clear benefits, challenges like node reliability, regulatory concerns, and user education remain. However, as privacy concerns grow, dVPNs are poised to become essential tools for online freedom.
What Is Decentralized VPN? - SecurityFirstCorp.com
Benefits of dVPNs with E2E Encryption Compared to Traditional VPNs
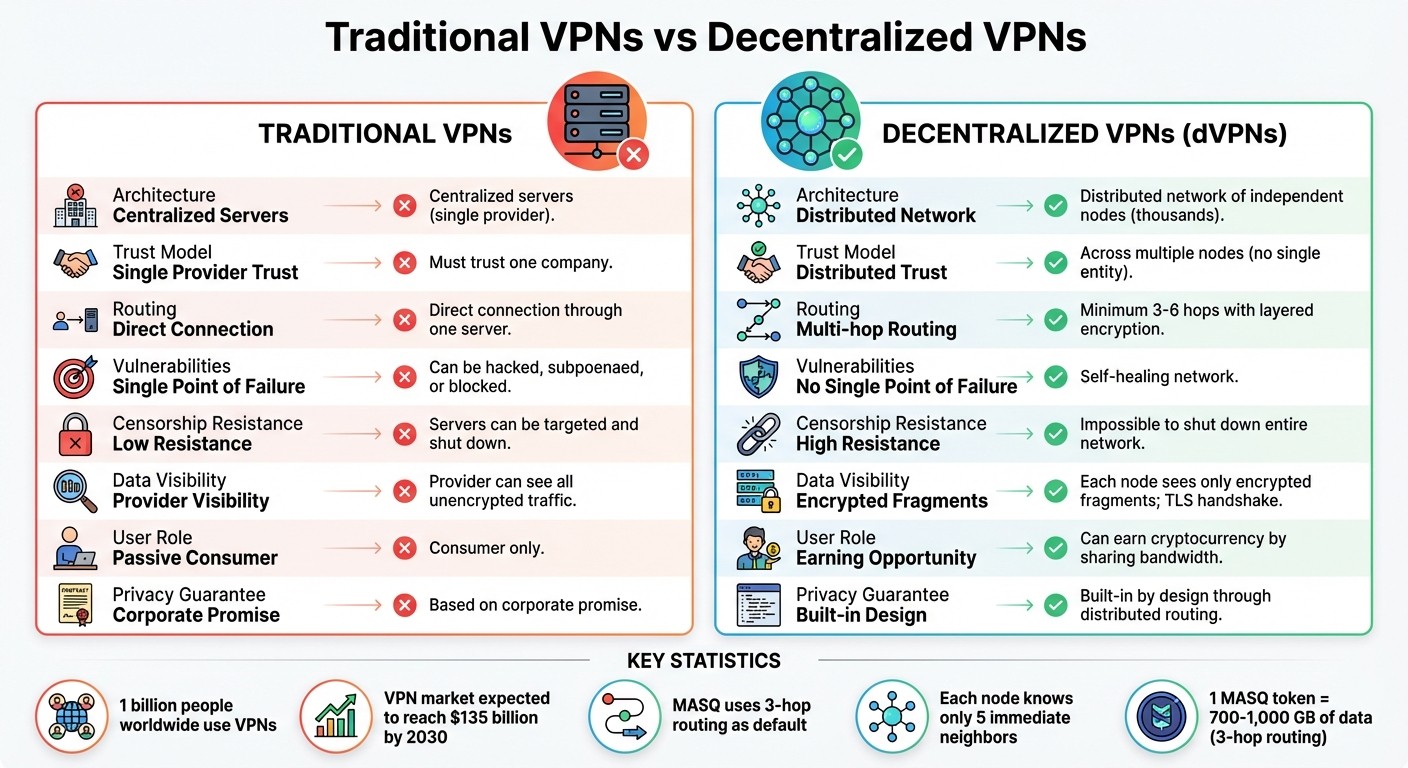
Decentralized VPNs vs Traditional VPNs: Key Differences in Privacy and Security
Enhanced Privacy and Security
Traditional VPNs require users to place full trust in a single provider. Decentralized VPNs, on the other hand, route your data through multiple independent nodes, with each node only accessing encrypted fragments of your traffic.
MASQ takes this a step further by using a direct TLS handshake between your browser and the destination. This ensures that even the exit node can only see encrypted data. As MASQ explains: "Even an evil, compromised exit Node still can't see your unencrypted data, the way a Tor exit node can". The network employs a minimum of 3-hop routing by default, adding multiple layers of separation to protect your identity and activity.
Another key feature is obscured routing. Decentralized VPNs can disguise data packets to make them look like standard HTTPS traffic. This method is highly effective against deep packet inspection techniques used by ISPs and government agencies, keeping your online activity hidden from surveillance.
This multi-layered approach not only strengthens privacy but also makes censorship far more difficult to enforce.
Resistance to Censorship and Decentralized Architecture
Unlike traditional VPNs, which can be disabled by targeting centralized servers or applying regulatory pressure, decentralized VPNs rely on thousands of independent nodes. This eliminates any single point of failure.
The MASQ network highlights this advantage with its self-healing capabilities. If certain nodes go offline or are blocked, the system automatically reroutes traffic using its automated Gossip protocols. Additionally, each node is designed to know only five direct neighbors, making it nearly impossible for attackers to map the entire network. As MASQ puts it: "The MASQ Network, once live, will grow to a point where it cannot be shutdown. No large entity or Government could censor the network from allowing users to access the freedom of the entire Internet".
Earn Rewards by Sharing Bandwidth
Decentralized VPNs also introduce a rewards model, allowing users to earn cryptocurrency by sharing their bandwidth. By enabling "serving mode", you contribute to the network's infrastructure by routing traffic for other users and, in return, earn tokens.
On the MASQ network, users can choose between a pay-as-you-go option or premium plans starting at $8 per month for annual subscriptions. These plans include "Earn Mode", which lets users offset costs by earning tokens. This model creates a self-sustaining ecosystem where consuming nodes pay for the data they use, and serving nodes are compensated. To kickstart this system, MASQ distributed tokens to over 25,000 wallets during its initial airdrop.
Core Technologies Behind dVPNs with E2E Encryption
Multi-Hop Routing for Added Security
Multi-hop routing is a clever way to boost online privacy by splitting trust across multiple independent nodes. Here’s how it works: when you use a decentralized VPN, your internet traffic doesn’t just take a single, straightforward path. Instead, it passes through multiple relays. The first node (entry node) knows your IP address but not where you're headed, while the last node (exit node) sees your destination but has no clue where the traffic started.
MASQ, for example, uses a 3-hop route as its default setup. This means your data travels through three separate nodes, each adding its own encryption layer. This layered approach ensures that no single node can piece together the full picture of your online activity. On top of that, MASQ employs a "neighborhood abstraction" system. Essentially, nodes only know about their immediate neighbors, making it impossible for any node to map the entire network or identify individual users. Even if one node is compromised, it can't expose the entire route or the other users.
To better understand how this works, here’s a breakdown of the key components that support dVPN security:
Component | Role in dVPN Security |
|---|---|
Control Plane | Manages node discovery, staking, and reputation on-chain to ensure transparency |
Data Plane | Handles the encrypted tunnel off-chain using protocols like WireGuard or QUIC |
Accountant Module | Tracks debts and credits between peers to prevent fraud without needing a central authority |
Gossip Protocol | Allows nodes to communicate and maintain the network without exposing personal details |
Beyond routing, blockchain technology plays a crucial role in ensuring transparency and trust.
Blockchain for Network Transparency and Trust
Blockchain acts as the backbone of decentralized VPNs, managing critical functions like node registries, payment verification, and accountability - all without interfering with your data traffic. This creates a system where trust isn’t placed in a single provider but is distributed across the network.
In the MASQ network, blockchain ensures that nodes are fairly compensated for routing traffic. As MASQ puts it:
"Blockchain technology provides the foundational aspects to secure this trustless transfer for service between protocol users, as payables and receivables between peers can be verified as executed transactions on the distributed ledger of the public blockchain."
This system also helps defend against attacks. For instance, every action on the network requires a small cryptocurrency payment. This cost discourages attackers from flooding the network with malicious requests. Additionally, if a node tries to tamper with payment records, other nodes can catch the inconsistency during routine network checks.
The MASQ network operates with a total token supply of 37,500,000 tokens. With 3-hop routing, users typically consume between 700 and 1,000 GB of data per $MASQ token.
Post-Quantum Cryptography for Future Security
As technology evolves, so do the threats. One emerging challenge is quantum computing, which could potentially crack today’s cryptographic standards. To stay ahead of this, dVPNs are exploring post-quantum cryptography. These advanced algorithms are designed to withstand the power of quantum computers, ensuring long-term security.
Another exciting development is clandestine routing, which adds an obfuscation layer to data packets. This makes VPN traffic look like random noise, making it far harder for adversaries to detect or analyze.
Additionally, the industry is shifting to modern transport protocols like WireGuard-over-QUIC and MASQUE-style tunneling. These protocols disguise VPN traffic as regular web browsing, allowing it to blend in seamlessly and bypass censorship efforts. Together, these advancements are shaping the future of secure and private online communication.
MASQ: A dVPN Solution with E2E Encryption
MASQ functions as a decentralized mesh network (dMeshVPN), connecting users through "neighborhoods" of nodes instead of relying on a single centralized server. It transmits data in encrypted "CORES" packages (Client-Origin-Relay-Exit-Server). When combined with a TLS handshake between your browser and the server, this ensures end-to-end encryption, keeping your data secure - even the exit node can't see unencrypted information. This unique setup powers several key features.
Multi-Hop Routing and Built-In Ad/Tracker Blocking
By default, MASQ routes your connection through 3 to 6 hops, layering encryption in a way that makes it nearly impossible to trace your origin or destination. Each node in a neighborhood knows only up to 5 immediate neighbors, making it impossible for any single node to map the entire network or identify users. Once six or more nodes are connected, routing begins automatically.
"MASQ protects your privacy by routing your connection through 3+ hops around the world." – MASQ Website
Additionally, MASQ blocks ads and trackers by default, preventing cross-site tracking and improving your browsing experience. Future updates aim to disguise MASQ traffic as regular data types, making it harder for ISPs to detect dVPN usage. These features make MASQ a powerful tool for secure, private browsing and pave the way for enhanced Web3 interactions.
Web3 Integration and Decentralized dApp Store
MASQ is designed with Web3 integration at its core. It includes multi-chain Web3 wallets that support MetaMask, Frame, and Rabby, enabling seamless interaction with blockchain services. The browser also features a curated Web3 App Library, giving users one-click access to popular blockchain platforms, decentralized applications, and metaverse experiences. On top of that, MASQ supports ENS domains, IPFS content, and decentralized services like Presearch, Filebase, and DM3.
Earn MASQ Tokens by Sharing Bandwidth
MASQ incentivizes users to contribute to the network by sharing bandwidth. By running a node and routing traffic for others, users can earn MASQ utility tokens (ERC-20). A peer-to-peer incentive system ensures tokens are transferred directly between users, while an internal Accountant Module keeps track of credits for traffic served and debts for traffic consumed. For example, 3-hop routing typically consumes 1 MASQ token per 700–1,000 GB of data.
For added privacy, it's recommended to use separate wallets for "consuming" (paying for data) and "earning" (receiving tokens) to avoid linking your identity to your node. MASQ tokens have a capped supply of 37,500,000, ensuring the network remains decentralized and secure while empowering users to participate.
MASQ offers flexible pricing options to suit different needs. You can opt for a pay-as-you-go model to top up your wallet as needed or choose a subscription plan. Monthly access costs $14, while an annual plan brings the price down to $8 per month. Both options include features like 1–5 hop dVPN access, faster speeds, and monthly data airdrops.
Challenges and Opportunities for dVPN Adoption
Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) promise enhanced privacy, but their adoption faces notable obstacles. By addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging solutions, the path forward becomes clearer.
Improving Node Reliability
Unlike traditional VPNs that rely on centralized data centers with guaranteed uptime, dVPNs depend on residential nodes. These nodes can go offline unexpectedly, leading to mid-session disruptions. For instance, VPN Gate, a well-known volunteer-run dVPN, operates approximately 5,529 nodes that handle over 1 TB of traffic daily. Maintaining consistent performance across such a decentralized network is no small feat.
To combat this, networks are implementing smart contracts and staking systems. These mechanisms require node operators to lock tokens as collateral, which can be penalized if nodes fail reliability checks or deliver corrupted data. Machine learning tools also play a role by analyzing metrics like round-trip times and throughput, allowing users to connect with the most dependable nodes. Additionally, self-healing protocols, such as gossip networks, automatically reroute traffic around offline or congested nodes, further bolstering reliability.
Addressing Regulatory Uncertainty
Operating in a decentralized framework often places dVPNs in a legal gray area. Exit node operators, whose IP addresses are publicly visible, can face legal risks, such as receiving abuse complaints or even being implicated in illicit activities. Recent cases show regulators targeting individuals involved in digital asset trading and money laundering, highlighting the potential liabilities even for privacy-focused tools.
However, technical advancements offer some protection. For example, MASQ employs TLS handshakes between the browser and the destination server, ensuring that even exit nodes cannot access unencrypted data. This setup allows operators to demonstrate they lack visibility into the content passing through their nodes, reducing their exposure to legal risks. For projects aiming to avoid scrutiny in heavily regulated regions like the US or EU, geofencing has become a key strategy to limit liability. These measures underline the importance of clear communication with users about how dVPNs function and the associated responsibilities.
Educating Users About dVPN Benefits
Beyond technical and legal hurdles, user education remains a critical factor in driving adoption. Many users are unfamiliar with dVPNs and their benefits. Surprisingly, 25% of commercial VPN providers lack even the most basic privacy policies, yet users often stick with these familiar, centralized models.
Educational initiatives should focus on the advantages of dVPNs, such as their decentralized trust model, which eliminates reliance on a single provider. Highlighting the opportunity to earn tokens by sharing bandwidth can also attract users eager to participate actively in the network. Simplifying the onboarding process is another priority. Tools like MASQ’s browser-based interface and pay-as-you-go payment options make the technology more accessible. Explaining features like multi-hop routing (with at least three hops) and kill switches can help users understand how to maximize privacy and prevent data leaks, making dVPNs a more appealing choice.
Conclusion
Decentralized VPNs with end-to-end encryption are reshaping the way we think about online privacy and security. As Casey Ford, PhD, Communications Lead at Nym, puts it: "The core benefit: It eliminates 'central points of failure,' meaning no single company can be hacked, subpoenaed, or coerced into handing over your data".
The technology driving dVPNs - like multi-hop routing that distributes trust across multiple relays and blockchain-based incentives for bandwidth sharing - creates a self-sustaining network. With over 1 billion people worldwide already using VPNs and the market expected to hit $135 billion by 2030, this shift toward decentralized systems is a direct response to growing concerns about corporate data collection and government surveillance. These systems don’t just offer privacy; they make it a fundamental part of how the network operates.
By design, dVPNs ensure privacy through features like distributed routing and ephemeral session keys, which eliminate centralized logging entirely.
For everyday users, this means censorship resistance, unrestricted access to geo-blocked content, protection from ISP tracking, and even token rewards for sharing bandwidth. Solutions like MASQ show how these advanced technologies can be packaged into straightforward tools, making online freedom accessible to everyone.
However, the road ahead involves overcoming challenges like ensuring node reliability, navigating regulatory uncertainties, and educating users. As more people come to understand that privacy should be a built-in guarantee rather than a corporate promise, decentralized VPNs with end-to-end encryption are poised to become indispensable for protecting internet freedom in an era of increasing surveillance.
FAQs
How do decentralized VPNs provide better privacy than traditional VPNs?
Decentralized VPNs (dVPNs) take privacy to the next level by removing centralized control and data storage from the equation. Unlike traditional VPNs that rely on servers managed by a single provider, dVPNs operate on a peer-to-peer network of independent nodes. This setup drastically reduces risks like data breaches, government surveillance, or logging since no single entity has complete control over user data.
What’s more, dVPNs often incorporate multi-hop encryption and routing, which makes tracking or intercepting online activity far more challenging for third parties. This added layer of security not only strengthens anonymity but also helps users bypass censorship. Even in regions with strict internet restrictions, dVPNs enable secure access to blocked content. Platforms like MASQ are leading the charge, using these technologies to create a safer, more private, and censorship-resistant online experience.
What legal risks should you consider when running exit nodes in decentralized VPNs?
Running an exit node in a decentralized VPN (dVPN) carries potential legal risks, as you could be held responsible for the traffic that flows through your node. For example, if someone uses your node for illegal activities like sharing copyrighted material or spreading harmful content, you might face legal consequences depending on the laws in your region.
Because dVPNs operate on peer-to-peer networks, issues related to data retention, privacy, and cybersecurity regulations can also arise. Authorities in countries with strict internet policies may scrutinize operators or issue legal requests. Understanding the legal responsibilities and staying informed about the regulations in your area is crucial before deciding to run an exit node.
How can I earn cryptocurrency by sharing my internet bandwidth on a decentralized VPN?
You can earn cryptocurrency by sharing your internet bandwidth through a decentralized VPN (dVPN) network like MASQ. When you join as a node in the network, you help transmit traffic for other users. In exchange for your contribution, you receive MASQ tokens, the network's native cryptocurrency.
The MASQ web3 privacy browser makes it easy to get started. With a simple toggle, users can decide whether to share their bandwidth. This peer-to-peer setup not only rewards participants but also strengthens online privacy, combats censorship, and promotes a decentralized, secure internet for everyone.




